给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
示例 1:
1
2
3
|
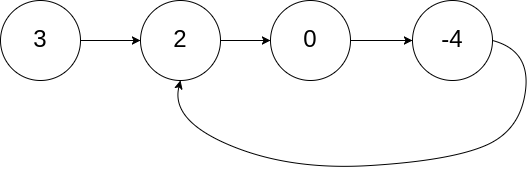
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
|

示例 2:
1
2
3
|
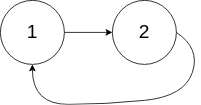
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
|

示例 3:
1
2
3
|
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
|

进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
思路
1
2
|
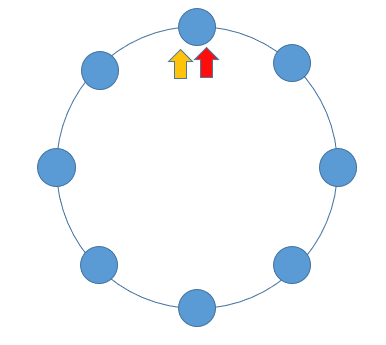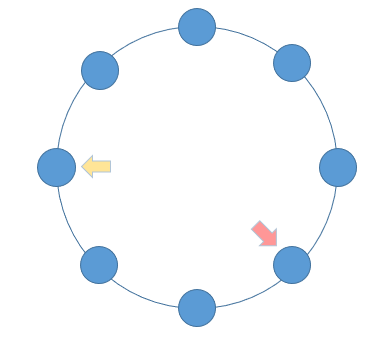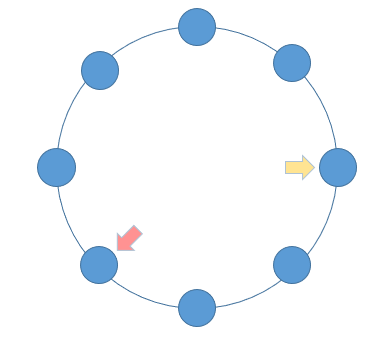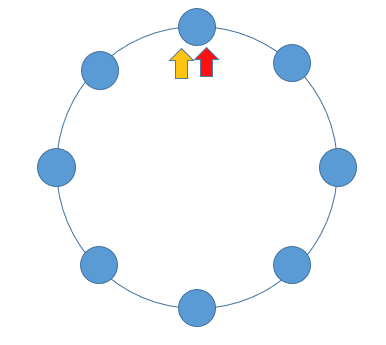
当一个链表有环时,快慢指针都会陷入环中进行无限次移动,然后变成了追及问题。想象一下在操场跑步的场景,只要一直跑下去,快的总会追上慢的。当两个指针都进入环后,每轮移动使得慢指针到快指针的距离增加一,同时快指针到慢指针的距离也减少一,只要一直移动下去,快指针总会追上慢指针。
根据上述表述得出,如果一个链表存在环,那么快慢指针必然会相遇。
|

代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
|
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020/7/22 22:19
# @Author : affectalways
# @Site :
# @Contact : affectalways@gmail.com
# @File : 141.py
# @Software : PyCharm
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020/7/16 22:27
# @Author : affectalways
# @Site :
# @Contact : affectalways@gmail.com
# @File : 0201.py
# @Software : PyCharm
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def hasCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if not head:
return False
fast = head.next
slow = head
while fast != slow:
if fast is None or fast.next is None:
return False
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return True
def create_link(tmp):
head = None
cur = None
for i in tmp:
node = ListNode(i)
if head is None:
head = node
cur = head
else:
cur.next = node
cur = cur.next
return head
def traversal_link(head):
cur = head
while cur:
print(cur.val)
cur = cur.next
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = create_link([1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1])
# traversal_link(head)
solution = Solution()
result = solution.hasCycle(head)
traversal_link(result)
|